SPA Module Development
Overview
Single-Page Application (SPA) frameworks are a newer alternative to server-side web development frameworks such as ASP.NET. SPA replaces the full-page updates of server-side frameworks, with small targeted updates of select page elements. This lightweight approach results in a faster and more responsive UI.
DNN's SPA module type simplifies the creation of modules that simulate traditional SPA applications and that use AJAX for all server interactions.
The SPA module framework consists of standard html, javascript and css by providing DNN-specific functionality and can be supplemented by other SPA frameworks, such as AngularJS, Knockout, and React.
SPA Module Architecture
In a SPA module, each HTML file loads the necessary JavaScript and CSS to properly render the UI. SPA modules also make AJAX calls to the business layer through the service layer. This architecture is similar to the mobile application architecture for Web Forms modules.
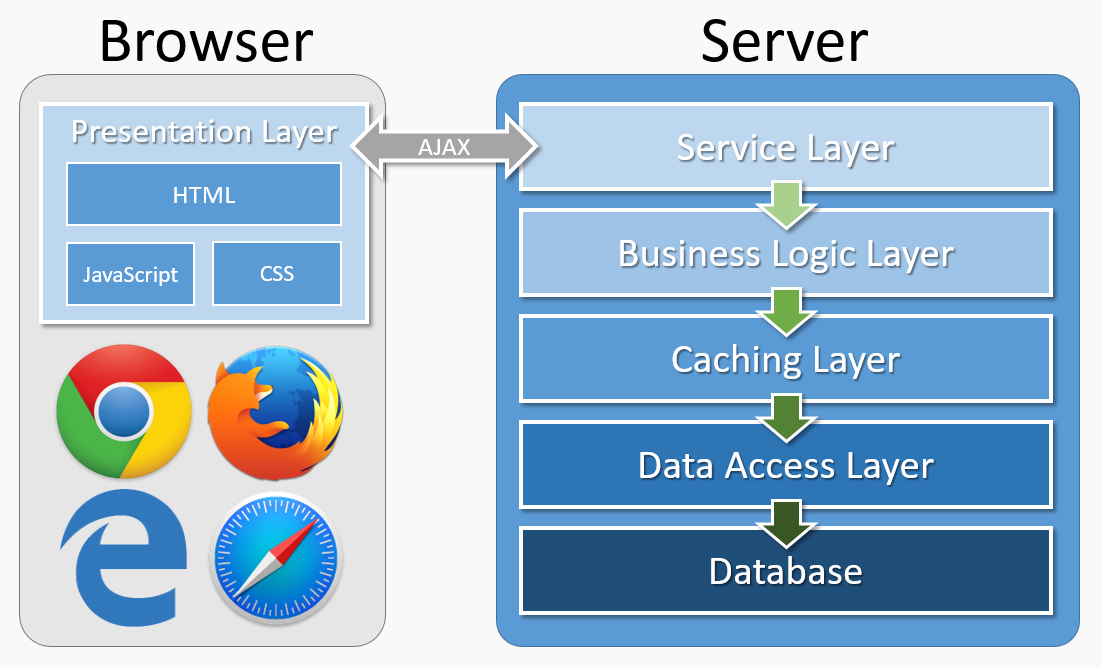
When a DNN page is requested, the framework looks up the requested module control in the module definition. In an SPA module, the module control identifies a specific HTML file. DNN tokens in the HTML file are replaced with site-specific data before the HTML is injected into the page.
Building SPA Modules
You have more development options available when building SPA modules compared to MVC modules. The server-side code can be created in Visual Studio as Web Application Project (WAP) or Web Site Project (WAP) types. (See Web Application Projects Versus Web Site Projects in Visual Studio.) Because the presentation layer is created with plain HTML, JavaScript, and CSS, its components can be built using any code editor.
You can choose to build the SPA module with all presentation layer code in one project and all server-side code in a separate project. This approach makes it easy to use different development tools that are optimized for server-side or client-side development.
Alternatively, you can use Visual Studio to create a single project that includes both server-side and client-side components. This approach leverages the MS Build system to easily package your module as part of your development process. The DNN SPA module template is set up for this approach.
Accessing DNN Features
Web Forms and MVC modules can easily access rendering-related DNN features because they are both server-side technologies. SPA modules use client-side technology and, therefore, require a different approach to access DNN features. Because a SPA module uses standard HTML, DNN provides custom tokens that can be included in the HTML to access data and APIs.
The following SPA module tokens can be used in your HTML:
JavaScript or JS : registers a JavaScript file with the Client Resource Manager. This token takes a json object with the following properties in order to register a specific javascript file.
- jsname : A named client script library that is included with Dnn. If the jsname is not provided, the path property must be provided. Valid values are names of javascript libraries defined in Extensions => Installed Extensions => Javascript Libraries
- path : The path to the javascript file to load (do not use jsname if you use this property).
- priority : The optional load order priority when multiple javascript files are loaded.
- provider : Optionally define the provider to use to inject the javascript file in specific places of the rendered html, valid values are :
- DnnBodyProvider : Will load the javascript file in the body of the html.
- DnnPageHeaderProvider : default if not provided, Will load the javascript in the page head section.
- DnnFormBottom : Will load the javascript file at the bottom of the global page form (near the bottom of the body).
- version : Optionally provide the version of the file to load if using the jsname property.
- specific Use in combination with the jsname to decide which version of the library to load if multiple versions are available, valid values are:
- Exact : The exact version.
- LatestMajor : The latest major version.
- LatestMinor : The latest minor version.
- Latest : The latest version registered.
Examples:
[JavaScript]: { jsname: "jQuery" }] [JavaScript:{ path: "~/DesktopModules/MyModule/scrpts/script.js"}]CSS : Registers a stylesheet with the Client Resource Manager. A local path or a url can be provided, in order to support both http and https, do not provide the protocol when using a url, it will automatically default to the protocol used in the page where it is injected. This token takes a json object with the following properties:
- path : The path or url to the css file.
- priority : An optional load order priority.
- provider : Can be used to optionaly enforce a specific injection provider, see available providers in the Javascrip token.
Examples:
[Css:{ path: "//maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/font-awesome/4.3.0/css/font-awesome.min.css"}] [Css:{ path: "~/Resources/Shared/components/CodeEditor/lib/codemirror.css"}]AntiForgeryToken : includes an anti-forgery token in the page to prevent Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) attacks.
Example:
[AntiForgeryToken:True]ModuleAction : identifies custom module actions. This token takes a json object with the following properties for the module action options
- controlKey : The control key as defined for that control in the module manifest
- icon : An optional path the to action icon, if not provided will default to the edit pencil icon.
- localResourceFile : The path to the localization resource file to use for the action title.
- securityAccessLevel : Defines the visibility permissions for this module action. Valid values are Edit, Admin, Host and View.
- title : The title of the action, if provided this way, the title will not be localizable (use titleKey instead if you need localization).
- titleKey : The name of the resource key to use from the localResourceFile to localize your action title.
Example:
[ModuleAction:{controlKey : "Settings", securityAccessLevel : "Edit", title: "Settings" }]Resx : includes a localized resource string in the page. This token takes a json object to define the localization key to get, valid properties are:
- key : The name of the localization key to get the localized value.
- localResourceFile : Can optionaly be used to specify from which localization file to use, if not provided, it will default to a localization resource file in the App_LocalResources folder next to the view contol with the same name. So if your view is
~/DesktopModules/MyModule/view.htmlit will look for~/DesktopModules/MyModule/App_LocalResources/view.resx.
Example :
<button id="cancelButton">[Resx:{key: "Cancel"}]</button>Request : includes the page-request query string in the page.
ModuleContext : includes a DNN module context property in the page. Supported module context properties include:
- ModuleId : The ID of the module.
- TabModuleId : The TabModule ID for the module.
- TabId : The page (tab) ID where the module is currently displayed.
- PortalId : The site (portal) ID where the module is currently displayed.
- IsSuperUser : Gets a value indicating whether the current user is a SuperUser (Host).
- EditMode : Gets a value indicating whether the module is currently in edit mode.
- SettingName : You can access a specific module setting by using the setting name, instead of a predefined property name.